1. Hex Bolt
Definition: A hex bolt has a six sided head
(hexagonal) and is used with a nut or tapped hole.
Use: Commonly
used in construction, machinery, and automotive applications for fastening
wood, metal, or other materials together. They provide strong and durable
connections.
2. Carriage Bolt
Definition: A carriage bolt has a round, smooth head
with a square section beneath it to prevent spinning during installation.
Use: Primarily
used in woodworking, such as furniture assembly or deck construction, where a
smooth, domed head is preferred for aesthetic or safety reasons.
3. Lag Bolt
Definition: A lag bolt is a heavy duty bolt with a
hex head, used for wood applications and has a coarse, sharp thread for strong
grip.
Use: Commonly
used in wood framing, decking, and heavy duty applications, such as securing
large beams and posts in construction.
4. U-Bolt
Definition: A U-bolt is shaped like the letter
"U" with threaded ends on both sides.
Use: Typically
used to secure pipes or tubes to surfaces or to attach round objects to a
framework, such as in plumbing, automotive, and marine applications.
5 Eye Bolt
Definition: An eye bolt has a loop (or
"eye") at one end and a threaded shank at the other.
Use: Commonly
used for lifting, towing, or securing cables and ropes in industrial or
construction settings. Eye bolts are frequently found in rigging and load
lifting applications.
6. J-Bolt
Definition: A J-bolt has a long shank and is bent
into a "J" shape with a threaded section on one end.
Use: Often
used as anchors in concrete or to hang or support structural components such as
walls, fences, and machinery.
7. Anchor Bolt
Definition: Anchor bolts are used to attach objects
or structures to concrete, with one end embedded in the concrete.
Use: Commonly
found in construction, used to secure structural elements like steel columns,
beams, or light posts to concrete foundations.
8. Flange Bolt
Definition: A flange bolt has a built in washer
(flange) under the head for better load distribution.
Use: Widely
used in automotive and industrial applications where a larger surface area is
needed for better pressure distribution without the need for separate washers.
9. Shoulder Bolt
Definition: A shoulder bolt, also known as a stripper
bolt, has an unthreaded, cylindrical shoulder between the head and the threaded
portion.
Use: Commonly
used in mechanical assemblies, pulleys, and linkages, where components need to
pivot or slide, such as in machinery and automotive systems.
10. Toggle Bolt
Definition: A toggle bolt is a fastener with spring
loaded wings that expand behind a hollow wall to distribute weight over a large
area.
Use: Ideal for
mounting objects to drywall, plaster, or other hollow walls, such as shelving,
light fixtures, and TV mounts.
11. Machine Bolt
Definition: A machine bolt is a fully threaded bolt
with a hex or square head used with a nut or in a tapped hole.
Use: Commonly
used in machinery and construction for securing metal parts together, providing
precise and strong connections.
12. Square head
Definition: A square head bolt has a four sided
(square) head instead of the more common hex shape.
Use: Typically
used in railroad construction, wood applications, or antique restorations,
where a traditional, rustic appearance is preferred or where extra grip is
needed during tightening.
13. T-Head bolt
Definition: A T--head bolt has a flat, T-shaped head,
allowing it to be placed into a slot or channel.
Use: Commonly
used in machine tool setups and construction, particularly in slotted rails or
tracks, where the bolt head fits into the track to secure other components.
14. Stud Bolt
Definition: A stud bolt is a threaded rod with no
head, typically used with two nuts, one on each end.
Use: Commonly
used in flange connections for piping systems, automotive engines, and
machinery, where both ends of the bolt need to be fastened.
15. Elevator Bolt
Definition: An elevator bolt has a large, flat, thin
head and is commonly used with a square neck to prevent rotation during
installation.
Use: Primarily
used in conveyor systems and grain elevators, where a wide, flat head is needed
to hold thin, soft materials securely.
16. Countersank Bolt
Definition: A countersunk bolt has a flat, conical
head designed to sit flush with or below the surface of the material it
fastens.
Use: Commonly
used in furniture and metalworking, where a smooth surface is desired without
the bolt head sticking out, such as in hinges or door handles.
17. Round Head bolt.
Definition: A round head bolt has a smooth, rounded
head and is typically used with a nut.
Use: Frequently
used in wooden applications and decorative projects, where the smooth, rounded
appearance is preferred for aesthetic reasons or where the bolt head needs to
be exposed.
18. Hanger Bolt
Definition: A hanger bolt has wood threads on one end
and machine threads on the other.
Use: Used to
secure objects to wood, such as in furniture assembly, hanging signs, or
suspending objects from wooden beams.
19. Plow Bolt
Definition: A plow bolt has a flat countersunk head
with a square neck to prevent turning, similar to a carriage bolt but designed
for heavier duty applications.
Use: Commonly
used in plow blades, heavy machinery, and construction equipment, where the
bolt needs to sit flush with the surface to avoid obstruction.
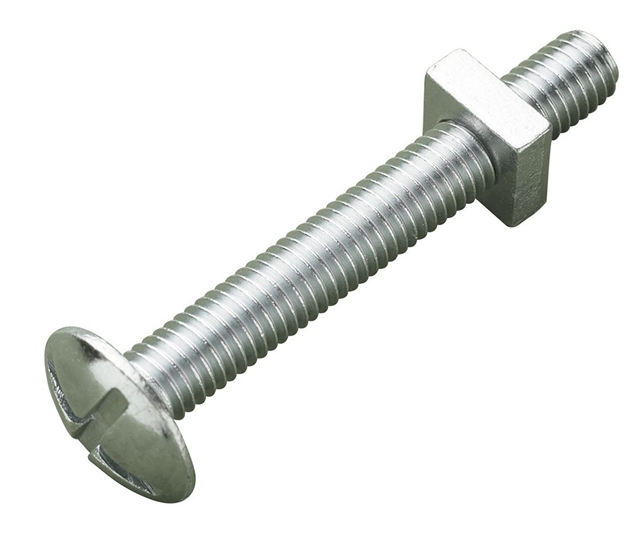
20. Roofing Bolt
Definition: A roofing bolt has a wide, flat head and
is usually fully threaded, designed to hold materials like metal sheets.
Use: Used
primarily in roofing applications, where the wide head helps distribute
pressure, securing roof panels or metal sheets together. They are also commonly
used in furniture assembly for similar reasons.




















Comments
Post a Comment
please give me your valuable feedback